Uveitis Treatment
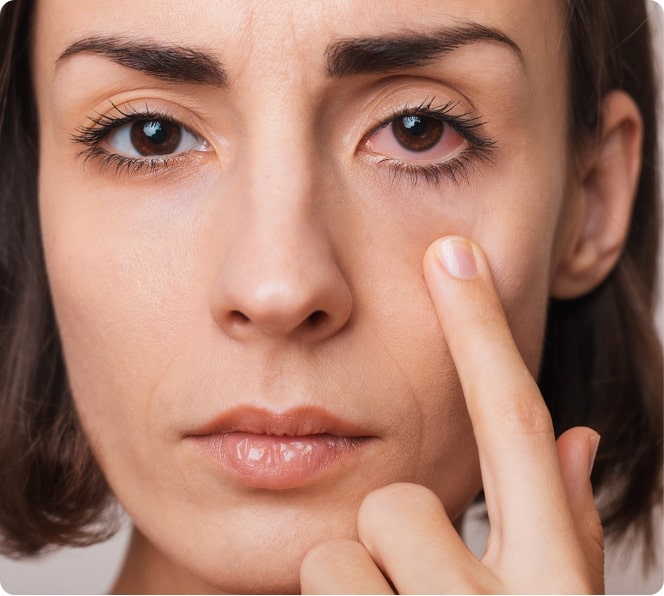

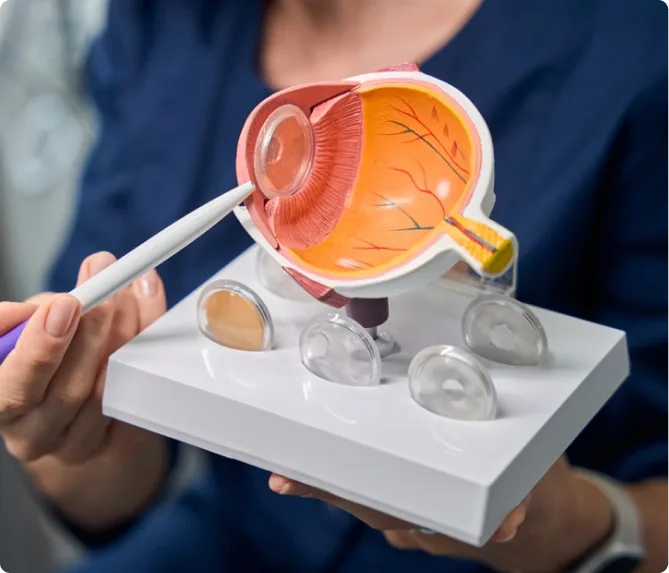
Uveitis is a term for inflammation or infection inside the eye. The condition can affect different parts of the eye, and your diagnosis may be more specific depending on the location:
- Iritis or Anterior Uveitis – Inflammation of the colored iris and surrounding tissue
- Vitritis or Intermediate Uveitis – Inflammation in the middle portion of the eye
- Retinitis or Choroiditis (Posterior Uveitis) – Inflammation in the back of the eye
- Uveitis can impact vision and may cause complications in other critical areas of the eye.
Why Early Diagnosis Matters
Because uveitis can arise from many causes, evaluation by a specialized ophthalmologist is essential. At Bascom Palmer Eye Institute, our physicians carefully examine your eyes to provide personalized treatment.
- If caused by eye injury or infection, treatment focuses on the eye.
- If linked to a systemic disease, managing the underlying condition may help control uveitis.
Symptoms of Uveitis
Symptoms often appear suddenly and may worsen quickly. Common signs include:
- Eye redness and pain
- Light sensitivity
- Blurred vision
- Dark, floating spots in your vision (floaters)
- Decreased vision
Causes of Uveitis
Uveitis can result from:
- Eye injuries or surgery
- Eye-specific inflammatory conditions (e.g., birdshot chorioretinopathy, pars planitis)
- Eye-specific inflammatory conditions (e.g., birdshot chorioretinopathy, pars planitis)
- Systemic inflammatory disorders (e.g., sarcoidosis, ankylosing spondylitis, juvenile idiopathic arthritis, Crohn’s disease)
- Infections (e.g., cat-scratch disease, herpes zoster, syphilis, toxoplasmosis, tuberculosis, Lyme disease, West Nile virus)
- Eye cancers (e.g., lymphoma)
Lifestyle factors: Studies show uveitis is more common and severe in people who smoke cigarettes, so quitting may help.
Untreated uveitis can lead to serious complications, including glaucoma, cataracts, or vision loss.
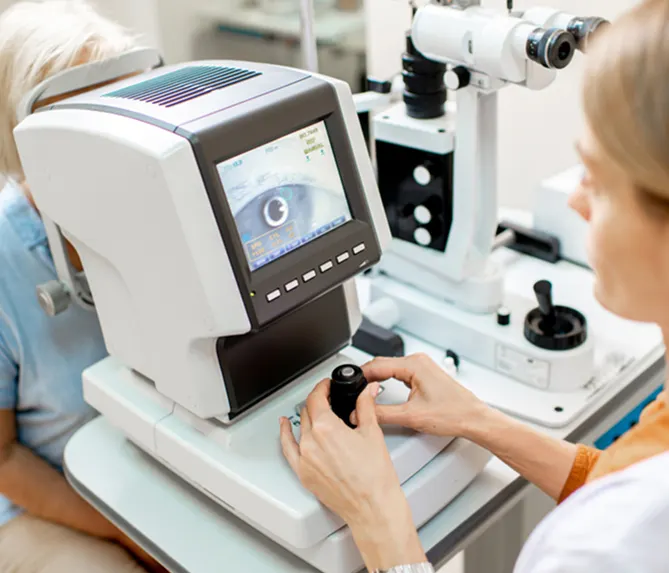
Tests and Diagnosis
Blood Tests & X-Rays
Standard blood tests and imaging, plus specialist referrals if needed.
Eye Fluid Analysis
Small samples from the front of the eye may help diagnose certain infections.
Eye Angiography
Fluorescent dye injected into a vein highlights blood flow in retinal vessels to detect inflammation.
Eye Photography
Modern imaging measures retina thickness and detects signs of inflammation quickly and painlessly.
Treatment Options
Treatment depends on the type and cause of uveitis:
Oral Medications
- Tailored to your specific condition, often including corticosteroids or immune modulators.
Injected Medications
- Steroid injections, slow-dissolving steroid pellets, or slow-release devices help control inflammation directly in the eye.
Vitrectomy
- Surgical removal of the vitreous (gel-like substance) may control intermediate uveitis or provide samples for precise diagnosis.
FAQ
What is uveitis, and why is it sometimes called 'silent inflammation'?
What are the types of uveitis, and how do symptoms vary?
How is uveitis diagnosed in a clinical setting?
What are the primary treatment strategies for uveitis?
Can lifestyle and prevention play a role in managing uveitis?
Our Doctors
No doctors available for this speciality.

Questions? We’re here to help.
Our appointment specialists are ready to help you find what you need. Contact us today.
